
As organizations increasingly rely on digital infrastructures to house all of their data, understanding concepts like the “attack surface” becomes essential to keeping security intact. But what exactly is an attack surface, and why should businesses be concerned about it? In this article, we’ll cover the fundamentals of attack surfaces in cybersecurity and how organizations can manage them to mitigate potential threats.
Defining the Attack Surface
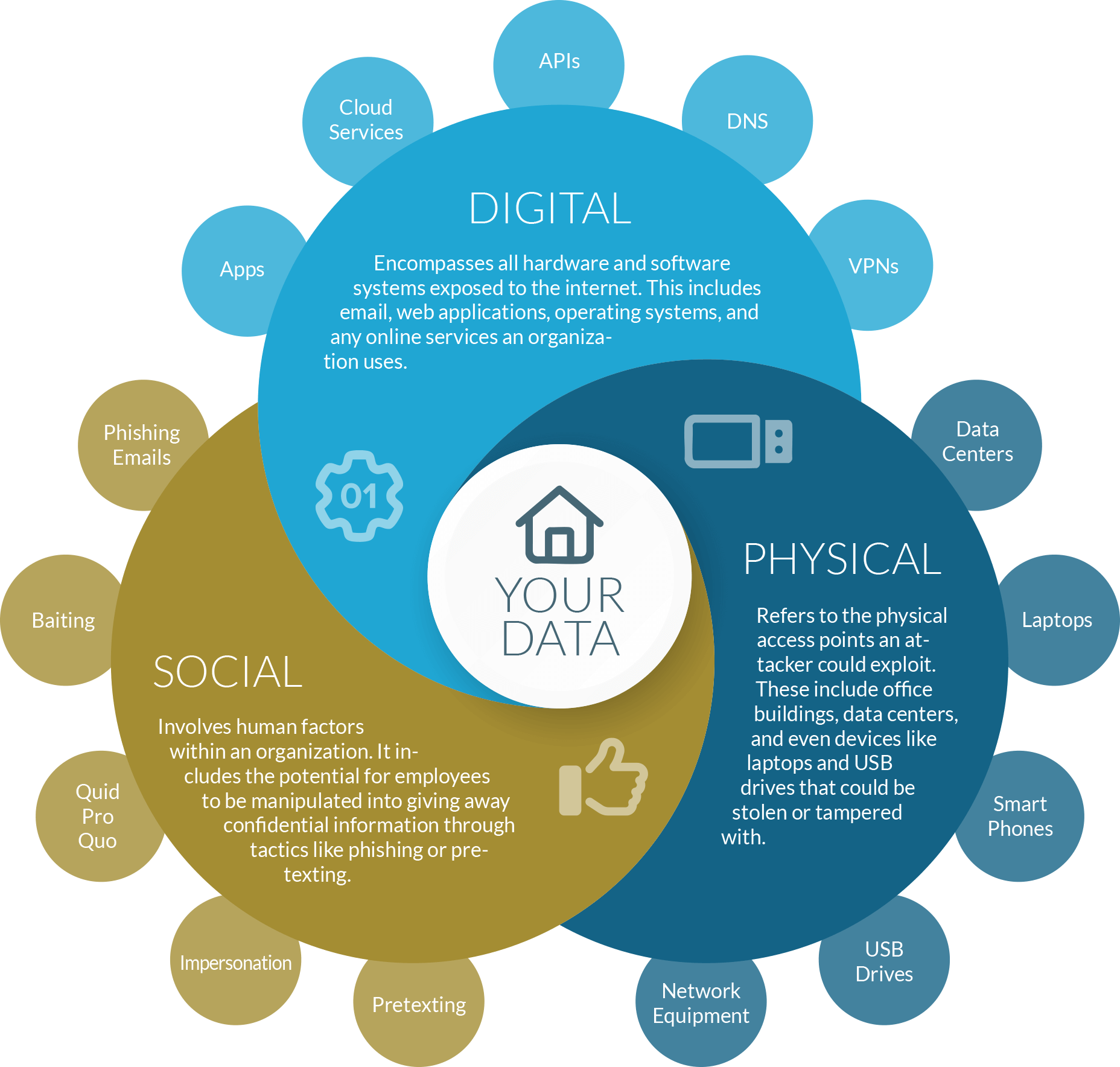
The attack surface of a system, network, or organization refers to the total sum of all possible points where unauthorized users (hackers) can attempt to infiltrate or extract data. Think of it as all the doors and windows of a house that needs securing against break-ins. The larger the attack surface, the more opportunities an attacker has to exploit vulnerabilities.
Attack surfaces can be categorized into three general types:
- Digital Attack Surface : Encompasses all hardware and software systems exposed to the internet. This includes emails, web applications, operating systems, and any online services an organization uses.
- Physical Attack Surface : Refers to the physical access points an attacker could exploit. These include office buildings, data centers, and even devices like laptops and USB drives that could be stolen or tampered with.
- Social Attack Surface : Involves human factors within an organization. It includes the potential for employees to be manipulated (social engineering) into giving away confidential information through tactics like phishing or pretexting.
Potential Breach Points
Even if all data is stored digitally, access to this data may be accessed across multiple entry points along the three Attack Surface types. Understanding where vulnerabilities exist is critical in formulating a strong defense. Here are various potential breach points within each category:
Digital Attack Surface
- Web Applications : Vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and inadequate input validation.
- Cloud Services : Misconfigured storage buckets or insufficient access controls.
- Mobile Applications : Insecure data storage, poor authentication mechanisms, and insecure communications.
- APIs : Lack of authentication, improper permissions, and insufficient data validation.
- Email Systems : Phishing attacks, malware-laden attachments, and spam.
- Network Protocols : Unsecured or outdated protocols that can be exploited for data interception or unauthorized access.
- Operating Systems : Outdated software with known vulnerabilities, unpatched security flaws.
- IoT Devices : Weak passwords, unsecured connections, and outdated firmware.
- DNS Infrastructure : Vulnerabilities to attacks such as DNS spoofing or poisoning.
- Remote Access Points : Unsecured VPNs, poorly managed remote desktop protocols, or home network vulnerabilities of remote workers.
Physical Attack Surface
- Data Centers : Unsecured or inadequately protected facilities that may allow unauthorized access.
- Office Buildings : Physical break-ins due to poor access controls or surveillance.
- Hardware Devices : Theft or loss of laptops, smartphones, USB drives, and other portable devices.
- Network Equipment : Routers or switches that are not physically secured.
- Supply Chain : Security weaknesses with third-party vendors or partners.
- Public Spaces : Company devices used in public areas where screens may be visible to unauthorized persons.
- Shared Workspaces : Areas shared with other entities where confidential discussions or displays may be overheard or seen.
Social Attack Surface
- Phishing Emails : Fraudulent communications designed to trick users into divulging confidential information.
- Spear Phishing : Targeted phishing attacks tailored to specific individuals to increase success rates.
- Pretexting : Creating a false scenario to obtain personal or sensitive information.
- Baiting : Luring victims with promises of goods to gain access to their systems or data.
- Quid Pro Quo : Offering a service in exchange for information.
- Impersonation : Pretending to be a trusted entity or colleague to extract information.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing) : Using phone calls to trick individuals into revealing personal information.
- Conferences and Events : Engaging attendees to extract information under the guise of networking or business discussions.
Why Is Understanding Your Attack Surface Important?
A comprehensive understanding of your attack surface is vital – for a number of reasons. By identifying potential vulnerabilities, organizations can take proactive steps to secure them before they are exploited. Knowing which entry points present the greatest risk allows IT teams to allocate resources effectively, focusing on the most vulnerable areas first.
Furthermore, many industries have strict regulations around data security, making it essential for companies to have a comprehensive understanding of their attack surface.
Finally, if a security breach does occur, a well-documented attack surface enables quicker and more effective responses, minimizing damage and recovery time.
Conclusion
In the realm of cybersecurity, understanding your attack surface is an essential prerequisite to following best practices effectively. By reducing your attack surface vulnerability, you decrease the chances of a devastating cyber attack, protecting not only your business operations but also the trust and confidence of your customers and stakeholders.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the need to be proactive and vigilant about cybersecurity has never been more urgent. Start by evaluating your organization’s attack surface, and implement strategies to minimize risk in your security posture.
Need help with your Attack Surface?

For assistance with the details surrounding your particular attack surface, speak with one of our cybersecurity experts to learn more about how Attack Surface Monitoring could help you.