
In a time where digital interactions are the norm, the need for secure online communication has never been greater. SSL/TLS certificates are critical for safeguarding sensitive information transmitted over the internet. But what exactly are these certificates, and why should businesses care? Let’s dive in.
What are SSL/TLS Certificates?
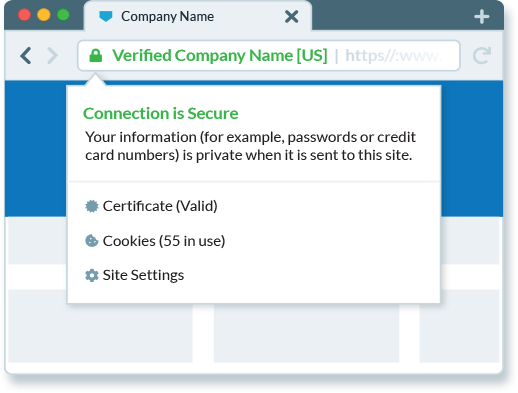
An SSL/TLS certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates the identity of a website and encrypts the information sent to it.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security), are protocols designed to encrypt data transmitted between a user’s browser and a web server. This ensures that any data exchanged remains private and integral, protecting it from eavesdropping or tampering by malicious actors.
The role of SSL/TLS Certificates in security
SSL/TLS certificates are crucial for data encryption. They transform the data being transferred into a format that is unreadable to anyone without the right decryption key. This ensures that sensitive information, such as credit card details and login credentials, remains protected from data breaches and unauthorized access.
Additionally, these certificates play a vital role in authentication by validating the identity of the website. This process confirms that users are interacting with a legitimate entity and not an imposter site, which is essential for building user trust in online transactions.
SSL/TLS certificates also ensure data integrity during transmission. They act as a safeguard by immediately terminating the connection if any interception or alteration is detected, maintaining the security and reliability of the data.
How SSL/TLS Certificates work
The process of SSL/TLS certificates involves an SSL/TLS handshake. When a user visits a website secured with SSL/TLS, the user’s browser first requests the server to identify itself. In response, the server sends back a copy of its SSL/TLS certificate.
The browser then verifies the authenticity of this certificate. If it is deemed trustworthy, the browser encrypts a session key using the server’s public key.
The server then decrypts this session key and, with this secure exchange, a secure, encrypted communication channel is established. This process ensures that the communication between the user’s browser and the server remains private and secure.
Types of SSL/TLS Certificates
- Domain Validation (DV): Provides basic encryption and only verifies ownership of the domain.
- Organization Validation (OV): Offers a higher level of validation by authenticating the legitimacy of the organization behind the domain.
- Extended Validation (EV): Offers the highest level of trust, providing a green address bar with the company name for added credibility.
Why businesses need SSL/TLS Certificates
- Boost Customer Trust: Visible security indicators like padlocks and HTTPS in the browser can enhance customer confidence, leading to increased trust and engagement.
- SEO Benefits: Search engines, like Google, can prioritize secure websites in their rankings, helping improve visibility and traffic.
- Compliance: Many regulations, such as GDPR and PCI-DSS, require encryption for handling personal or financial data, making SSL/TLS certificates a compliance necessity.
Conclusion
SSL/TLS certificates are vital components in the architecture of modern cybersecurity, providing encryption, authentication, and data integrity. As online security threats continue to evolve, businesses must prioritize the implementation of these certificates to protect their customers and their operations.
Questions about your SSL / TLS Certificates?

Our Team is here to help you understand, set up, and implement SSL/TLS Certificates into your business. Find out how our Certificate Monitoring Service can help with your unique security posture.